Vitamin E gamma tocopherol lung controversy
 Thursday, February 24, 2022 at 11:39AM
Thursday, February 24, 2022 at 11:39AM DOES GAMMA TOCOPHEROL CAUSE LUNG DAMAGE? (Questioning Analysis)
The CARDIA study ref followed 5000 subjects over 20 years with one arm later looking at the effects of alpha tocopherol and gamma tocopherol on lung function. The conclusion was that gamma tocopherol damaged lungs while alpha tocopherol protected lungs. ref Here is the author's logic. After 1940, the American diet changed going from butter and lard to soy and corn oil margarine. This increased the amount of gamma tocopherol in the diet to levels higher than before this change. At the same time, lung and asthma disease cases started to rise. Adding in a report that showed lung damage in animals fed gamma tocopherol versus protection when fed alpha tocopherol, the authors concluded that gamma tocopherol was the guilty party responsible for the increase in asthma. The mechanism thought responsible was the action of protein kinase C alpha, increased by gamma tocopherol that promoted inflammation in the lungs by allowing white blood cells to go into lung tissues leading to inflammation. Here is easy read ref. In contrast to these findings, here is another animal study showing just the opposite that the gamma form of E has the greatest anti-inflammatory response. ref ref
 SIDEBAR: The results of these "observation" studies or theories might be correct. But like many other nutrients, gamma tocopherol might influence pathways in two directions, one favorable and one not. Plus, it could also have different influences at high levels in test tubes or animals than inside the human body at normal levels. ref What determines which pathway happens depends upon other factors also present, such as the level of alpha tocopherol in this case, which in the animal lung study had opposing forces to balance. OR...
SIDEBAR: The results of these "observation" studies or theories might be correct. But like many other nutrients, gamma tocopherol might influence pathways in two directions, one favorable and one not. Plus, it could also have different influences at high levels in test tubes or animals than inside the human body at normal levels. ref What determines which pathway happens depends upon other factors also present, such as the level of alpha tocopherol in this case, which in the animal lung study had opposing forces to balance. OR...
OR, it could be the that gamma works better against one type of radical while alpha works against another type, nitrogen versus oxygen, so the results would depend upon which oxidation form was dominate. Another difference is that alpha tocopherol prevents radical formation while gamma works to reduce free radicals after they are formed. BUT, the study could also have made mistakes in application of dietary changes that a second more advanced study discovered. Here is an animal study showing positive gamma and delta tocopherol effects. ref 2 And another positive study on reduced inflammatory markers here. Plus check out this reference showing greater protection from gamma and delta tocopherol on breast cancer risk.
The manner in which this lung damage finding was reported in the media sent a fear into vitamin consumers to question the vitamin E form and source they were consuming. It was reported that soy, corn, and canola oils were the source of the gamma form of E. While in foods the sources tell what form of the vitamin E family is most abundant, this has nothing to do with the form of vitamin E in supplements, or on the source. 98% of supplement vitamin E is from soy oil, but the gamma tocopherol fraction is changed entirely or almost all into the alpha tocopherol form, just like the body also has the ability to do if more alpha tocopherol is needed. There is more to this issue then the obvious. In fact, another later study going into far more detail on protein kinase C alpha also revealed just the opposite. Below is copied part of that study ref:
"Research on vitamin E including potential protective effects on asthma has mostly focused on αT (alpha tocopherol), the predominant form of vitamin E in tissues. Although severe αT deficiency appears to modulate airway allergic inflammation [1], inconsistent outcomes have been reported in clinical and animal studies regarding the role of α-T supplementation in airway diseases [2-6]. On the other hand, studies by us and others strongly suggest that other forms of vitamin E including γT (gamma tocopherol), the major form of vitamin E in US diet, appear to have unique properties that are important to disease prevention or treatment [7, 8]. We have shown that γ-T, δ-T and γ-TE as well as their metabolites are more potent than α-T in inhibition of cyclooxygenase- and 5-lipoxygenase-catalyzed eicosanoids in cell-based studies and in an inflammation model in rats [9-13]. γ-T is also better than α-T in scavenging reactive nitrogen species and attenuating inflammation-related damage [11, 14, 15]. γT administered by nebulization is shown to improve pulmonary function in sheepwith burn and smoke inhalation injury [16]. Recently, we have demonstrated that γ-T supplementation inhibited ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in an asthma and allergic rhinitis model, respectively, in Brown Norway rats [17, 18]. In these studies, γ-T supplementation led to marked decrease of airway eosinophil infiltration and reduced proinflammatory cytokines [17, 18]. Despite these exciting findings, the mechanism(s) underlying γ-T-exerted inhibition of eosinophilia was not fully understood."
ANALYSIS: It looks like the side study in CARDIA missed something important. They thought that as canola and soy oils increased at same time as Asthma that the gamma tocopherol content of the oils was the guilty party. Especially since the rat study supported the damaged lungs from giving extra gamma taocopherol. The foods like soy and corn oil that have increased levels of gamma also use up more alpha to protect the oils against oxidation. This would increase the gamma content as a ratio with alpha.
Then along comes this new study that shows gamma tocopherol is more effective in reducing inflammation in asthma than alpha tocopherol. Plus, other emerging dietary factors that also occurred at the same time, such as changes reducing omega 3 and increasing omega 6, might have played a major role in creating inflammation. ref ref It might very well be that the two E members have opposing influences (even on each other). Maybe that is why nature made gamma tocopherol able to convert into alpha tocopherol in the body. In nature they are usually found together and rarely just one or the other is present as is found in most supplements. Balance may be Nature's protective mechanism. ref
Which is the TRUTH? Could it be that it was the change to vegetable oil's omega 6 content that was really the inflammation trigger leading to lung impairment of the canola and soy diets (omega 6) versus the sunflower and olive oil diets with mostly omega 9 as 85% monounsaturated fat. Or was it the dietary reduction from 18 pounds to 4 pounds a year for butter consumption, also a source of omega 3 and vitamin A for heart health, that was the real villain? Important >ref* ref
Did greater hydrogenated vegetable oils and the resulting increase in trans fats with the associated reduction of vitamin K play a role. It would be a tragedy if people lost out on the benefits of the whole family of vitamin E from the false reports of lung damage by gamma tocopherol in this one study, especially since it was just an observational report of just looking at the facts and assuming an influence. Not that this study is without any value, it does give rise to the fact that a balance is needed between vitamin E family members as would exist in nature without man's interference. ref The exact beneficial ratios between the vitamin E family members, unknown at this time, would be achieved over a period of time naturally by the use of a variety of consumed natural whole foods.
BENEFITS OF GAMMA TOCOPHEROL
ON bone health:
Higher Gamma tocopherol protects and builds more bone than higher alpha tocopherol. ref Here is conclusion from study: "Vitamin E supplements in the form of alpha-tocopherol suppress serum gamma-tocopherol levels and may have negative effects on bone formation. Further research is needed to investigate the potential anabolic (building) effect of gamma-tocopherol from food sources on bone."
ON cancer: While this is just a lab study, the results...ref ..ref
Here is perhaps the greatest benefit of gamma tocopherol on cancer. ref Gamma, but not alpha tocopherol, increases the death rate of cancer cells. Gamma tocopherol significantly protects against cell damage leading to tumors, and exhibits greater ability to destroy cancer cells than alpha tocopherol.
Would you rather prevent and destroy cancer cells or suffer 10% percent reduction in lung function, if indeed the first study was correct, which the second study questioned?
ON heart disease:
It is interesting to note this fact. Scientists wanted to find out the body levels of the vitamin E forms between healthy people versus people with heart disease. The amazing findings revealed that the d-alpha tocopherol levels were the same. Thus, it appears consuming d-alpha tocopherol vitamin E may not be related to the issue of prevention or influence on heart disease as some studies have shown. The finding that is of more significance, it was gamma tocopherol levels that were reduced in heart patients. Remember, the body has the ability to convert gamma tocopherol into the d-alpha tocopherol form if needed. So, it could very well be that d-alpha is needed in heart disease, but levels are maintained by gamma conversion so it is gamma that is low and needs to be supplemented as it has separate and unique functions that would be limited by this conversion to maintain alpha levels. Correct amounts have yet to be determined since studies are lacking to find this out. ref
*Chart for this reference showing the change in omega 3 to omega 6 from the butter and lard to soy and corn oils partly responsible for major inflammatory shift.
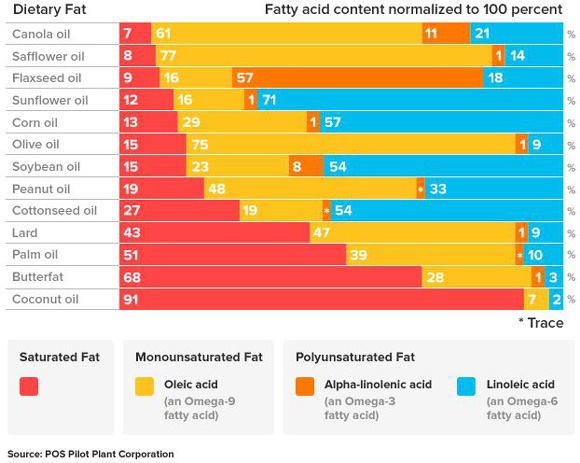
For Clarification Concerning Omega Fats:
It needs to be made clear that both omega 3 and omega 6 fats have vital roles to play in health. While one pathway for omega 6 is involved in generating inflammatory responses, this is a necessary and positive action for certain body situations. It is within a certain range that the balance between omega 3 and 6 is critical to control this inflammatory response to just when needed. The amount of Omega 3 as EPA is the nutrient the body uses to control the omega 6 pathway that goes into this inflammatory action potential. There are a couple of other healthful pathways for omega 6 fats. Also of critical importance is the protection of PUFAs by an antioxidant load including vitamin E, and not just d-alpha tocopherol alone, but the whole family of vitamin E players. (D-alpha, D-Delta, D-Beta, and D-Gamma in both tocopherol and tocotrienol configuration)
In the past, this omega balance was maintained. But, with modern food processing and production methods, the balance point was exceeded largely due to the increased use of higher omega 6 containing vegetable oils and beef from cattle raised in grain feedlots. Grain feeding of cattle changes the type of bacteria predominate in the cow's gut so that it does not produce enough omega 3 fat. It is just that simple. This event increased omega 6 fats and reduced omega 3 to the point where the body lost control of balancing mechanisms to try and compensate. Uncontrolled inflammation conditions became chronic and increased inflammatory related diseases, such as Cardiovascular and also some cancers.
A vital piece of this inflammatory puzzle has been largely left out of most discussions. Grain lot feeding of cattle also diminished the amount of vitamin E family as well as almost completely eliminated the natural carotenoids cows would get from pasture grass. The cattle industry gives feedlot cows vitamin E supplements as a way to improve the anti-oxidant status of beef so it will not spoil as quickly. This eliminates the absorption of the little beta carotene in this type of diet, so it also has to be given in a limited controlled amount to prevent the yellowing of beef fat. ref
Can you see how these nutritional changes in beef of fat types and anti-oxidant vitamins might have dramatically influenced health? And still do to this very day. These facts are responsible for the resurgence of the grass-fed beef movement.
WHAT ABOUT TOCOTRIENOLS?
Here is a study showing that gamma-tocotrienols inhibit inflammation in lungs while gamma tocopherol may increase.
Reader Comments